FAQ
We’ve compiled some of the most frequent questions that are asked. If you have a question that is not listed, please reach out to us today.
What is ATSC 3.0
The IP-based ATSC 3.0 ushers in a large-scale advance for broadcasting technology that brings together the capabilities of over-the-air (OTA) broadcasting, the internet, and a host of additional use cases that provide the opportunity for broadcasters to generate new revenue streams.
The combination of ATSC 3.0 and gains in compression and frequency management made since the original digital television revolution introduces another leap forward. In the ATSC 3.0 world, a 6 MHz frequency channel using current ATSC 1.0 transmission parameters
and covering a similar area will hold an estimated capacity of 26 Mbps (enabled via 256 QAM)—about 33% more than the 19.4 Mbps capacity of ATSC 1.0 standards. This additional space enables a move toward 4K delivery because of the increased channel capacity and compression capability for a primary content stream.
ATSC 3.0 can also agnostically leverage any transmission method to deliver content and allow the seamless move from one transmission mechanism to another based on the receiving device, product reach, or service and signal capabilities.
Is ATSC 3.0 offered outside the United States?
While PEAK3 is primarily focused on ATSC 3.0 edge deployments in North America, it is offers in areas around the world.
- South Korea
- India
- Europe (certain areas)
- Australia
- Brazil
- Jamaica
What is Multicast?
Multicast distribution is a key example of wholesale as a service or distribution as a service in action. Multicast distribution uses the capabilities enabled by ATSC 3.0 to automate datacasting in a one-to-many format, or multicasting, to IoT and other edge devices.
Through PEAK3, multicast can be enabled on the edge. Architecture that incorporates ATSC 3.0 with new cloud, SD-WAN, and orchestration technologies allows enterprise companies to rent spectrum dynamically and when needed.
Largescale software updates for “edge-heavy” industry (like Building/Industrial Automation, Automotive, and Critical Infrastructure) are clear examples of multicasting at work. Electric and autonomous vehicles require the continuous ability to update software for new functionality, bug fixes, and navigation. For autonomous vehicles in particular, safety is at stake, and car manufacturers must update software within hours—not days or months. Once hundreds of thousands of vehicles requiring software updates are on the road, broadcasting a multi-gigabit software update over a unicast network will cause network bottlenecks as periods of accommodation for terabits of traffic will be needed. As an alternative, PEAK3’s ATSC 3.0 broadcasting service enabled by multicasting will make it possible to simultaneously deliver software updates to infinite numbers of IoT devices such as smart vehicles.
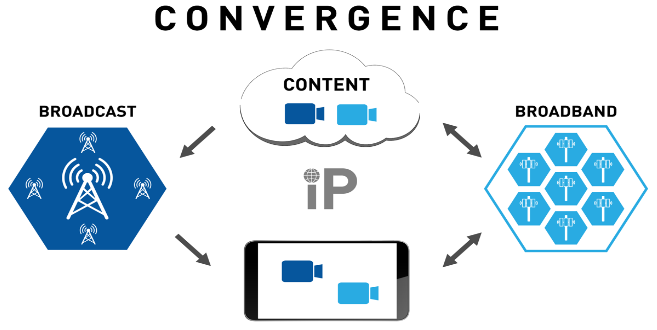
Does ATSC 3.0 Compete with 5G?
Transformation of the cellular industry to 5G and its Convergence with broadcast industry to the new ATSC 3.0 digital transmission standard1 is the biggest change in content transmittal since the emergence of the commercial internet. Connectivity will form the backbone of the economy in this new era of communication. In this era, the convergence of multiple technologies leads the next wave of digital transformation, opening new choices, expectations, and challenges to clients, providers, and distributors.
Expanded access and choices on the client side provide each client with multiple connectivity options—ranging from 5G to ATSC 3.0 to Wi-Fi. In this choice-rich environment, broadcast content consumers will expect the ability to tailor their content streams and receive latency-free content. At the same time, non-traditional “customers” such as embedded software providers, connected device manufacturers, and “autonomous everything” services will use the same wireless distribution pathways traditionally found in broadcast networks. Content providers and distributors will have many ways to transmit digital assets and data to targeted or mass audiences and will need effective, reliable,
and cost-efficient methods to do it.
Harnessing the potential of multi-technology convergence in this choice-rich environment will mandate that service providers have access to an optimal mix of the best and most efficient technologies (5G, broadcast, broadband, or even satellite) and the knowledge of how to optimally push traffic over each, when and where needed.
Can we download a whitepaper to learn more?
Yes, please feel free to take a deeper dive by downloading our whitepaper.